


What is
PBC?
PBC is a leading cause of liver transplant for women.



PBC is a leading cause of liver transplant for women.
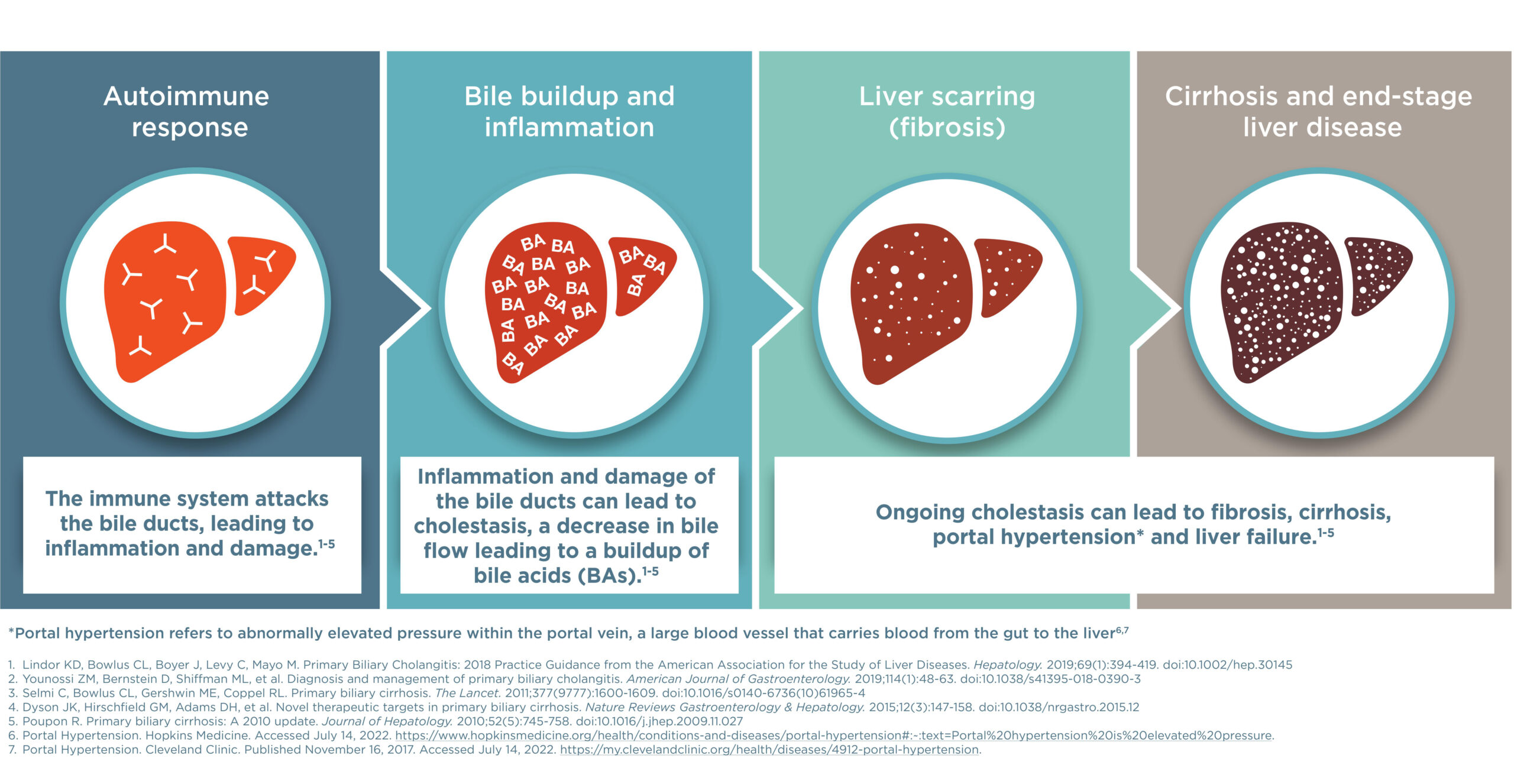
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a rare liver disease that is caused by an autoimmune reaction. The autoimmune reaction damages bile ductsA tube-like structure in the liver that transports bile to the small intestine to help with digestion. in the liver. Bile ductsA tube-like structure in the liver that transports bile to the small intestine to help with digestion. are tube-like structures that carry bile from the liver to the intestine to help with the digestion of food.
When bile is not able to move through the bile ductsA tube-like structure in the liver that transports bile to the small intestine to help with digestion., it collects in the liver and causes damage. PBC is progressive, which means that the damage gets worse over time. Starting with inflammation, the damage can cause fibrosisExcess connective tissue in an organ that can lead to damage., and then cirrhosisSevere scarring of the liver.. In some cases, cirrhosisSevere scarring of the liver. can lead to liver failure.
The rate of damage caused by PBC varies in different people. If left untreated, PBC can get significantly worse in 2 years, making it important to get an early diagnosis to start treatment as quickly as possible.
Once someone is diagnosed with PBC, it is important to talk to a doctor about getting regular liver function tests to track the progression of the disease.
It is estimated that 90% of people who are diagnosed with PBC are women. Many people who are diagnosed with PBC are between 40-60 years of age. It is important to note, however, that men and young women can also develop PBC.
The most common symptoms of PBC are pruritus, or itching, and fatigue. Some people with PBC can also experience dry eyes and mouth. For people with more advanced PBC, serious liver damage can cause jaundiceThe yellow appearance of the skin and eyes that can be caused by liver failure., or a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Many people do not experience any symptoms at the beginning of their PBC. The only sign that they have PBC is that abnormalities appear in their liver function test results.
Doctors can test for PBC by taking blood samples and measuring certain chemicals related to liver function. The tests will show if there are elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP)One of several chemicals in the body that can be used to diagnose primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) and track the progression of the disease. and if antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs)A chemical in the body that can be used to diagnose PBC. are present, which can be indicators of PBC.
You are now leaving Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ corporate website and entering a site intended for U.S. audiences only.
You are now leaving Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ corporate website. Intercept does not control or endorse the content of this external site.
The link you have selected will take you outside of Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ corporate website.
The site you will be entering is intended for U.S. audiences only.
If you are a healthcare provider looking for product information, visit ocalivahcp.com.
You have selected a link that will take you to a site maintained by a third party who is solely responsible for its contents. Intercept provides this link as a service to its website visitors. Intercept is not responsible for the content or the privacy policy of any third party websites.
Close this window to return to Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ site or click ‘Continue’ to proceed.
United States (US)
European Union (EU)
Canada
Israel
Switzerland
Australia
Liechtenstein
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Exploring Racial Differences and Disparities in PBC Care
Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a wholly owned biopharmaceutical subsidiary of Alfasigma S.p.A., announced its decision to voluntarily withdraw OCALIVA® (obeticholic acid) from the US market for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), a rare, progressive liver disease.
Healthcare professionals can contact Medical Information at medinfo@interceptpharma.com or call 1-844-782-4278. Patients should talk to their healthcare professionals and may also contact Intercept's Patient Support Services (Interconnect) at 1-844-622-4278.
For all other inquiries please visit: https://www.interceptpharma.com/
Please click here for Full Prescribing Information and Medication Guide for OCALIVA.